Tetanus
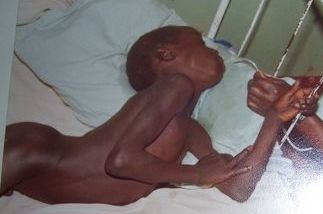 Tetanus is a condition of toxaemia due to absorption of soluble toxin from the wound contaminated with clostridium tetani. The word tetanus comes from the Greek, tetanos, which is derived from the word teinein meaning stretch.
Tetanus is a condition of toxaemia due to absorption of soluble toxin from the wound contaminated with clostridium tetani. The word tetanus comes from the Greek, tetanos, which is derived from the word teinein meaning stretch.
 Tetanus is a condition of toxaemia due to absorption of soluble toxin from the wound contaminated with clostridium tetani. The word tetanus comes from the Greek, tetanos, which is derived from the word teinein meaning stretch.
Tetanus is a condition of toxaemia due to absorption of soluble toxin from the wound contaminated with clostridium tetani. The word tetanus comes from the Greek, tetanos, which is derived from the word teinein meaning stretch.
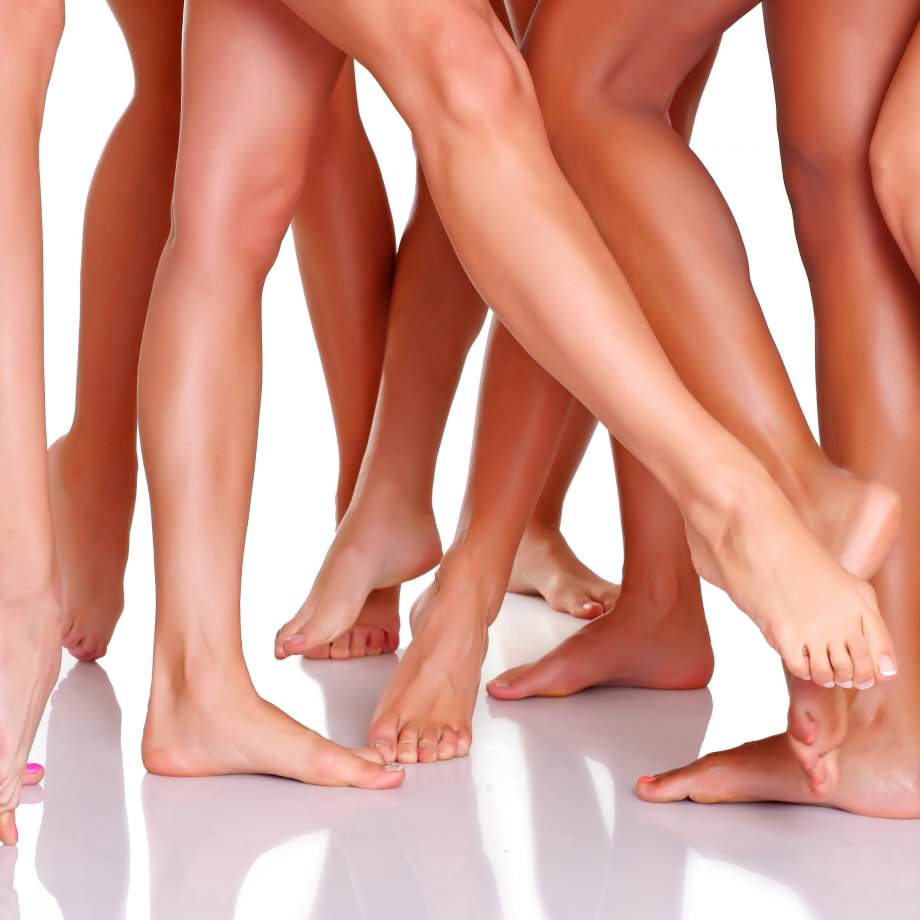 The single most common cause of vein disease is heredity. Approximately 70% of all patients with varicose veins have a parent with the same condition. Additional factors leading to varicose veins include gender, pregnancy, and age. Other factors may speed up the development of this disease and make the veins worse, such as prolonged standing, obesity, hormone levels, and physical trauma.
The single most common cause of vein disease is heredity. Approximately 70% of all patients with varicose veins have a parent with the same condition. Additional factors leading to varicose veins include gender, pregnancy, and age. Other factors may speed up the development of this disease and make the veins worse, such as prolonged standing, obesity, hormone levels, and physical trauma.
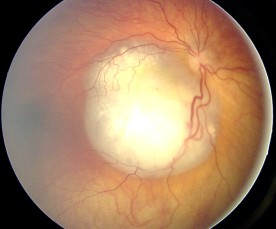 Retinoblastoma is the most common primary ocular malignancy (eye cancer) of childhood. The tumor develops from the immature retina - the part of the eye responsible for detecting light and color.
Retinoblastoma is the most common primary ocular malignancy (eye cancer) of childhood. The tumor develops from the immature retina - the part of the eye responsible for detecting light and color.
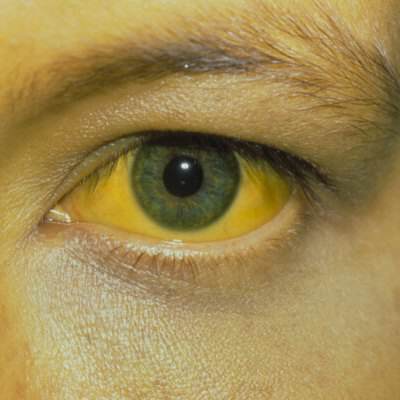 Hepatitis is a general term meaning inflammation of the liver and can be caused by a variety of different viruses such as hepatitis A, B, C, D and E. One of the more common causes of acute hepatitis is hepatitis A virus (HAV). Hepatitis A is contracted at least 100 times more frequently than typhoid fever or cholera.
Hepatitis is a general term meaning inflammation of the liver and can be caused by a variety of different viruses such as hepatitis A, B, C, D and E. One of the more common causes of acute hepatitis is hepatitis A virus (HAV). Hepatitis A is contracted at least 100 times more frequently than typhoid fever or cholera.
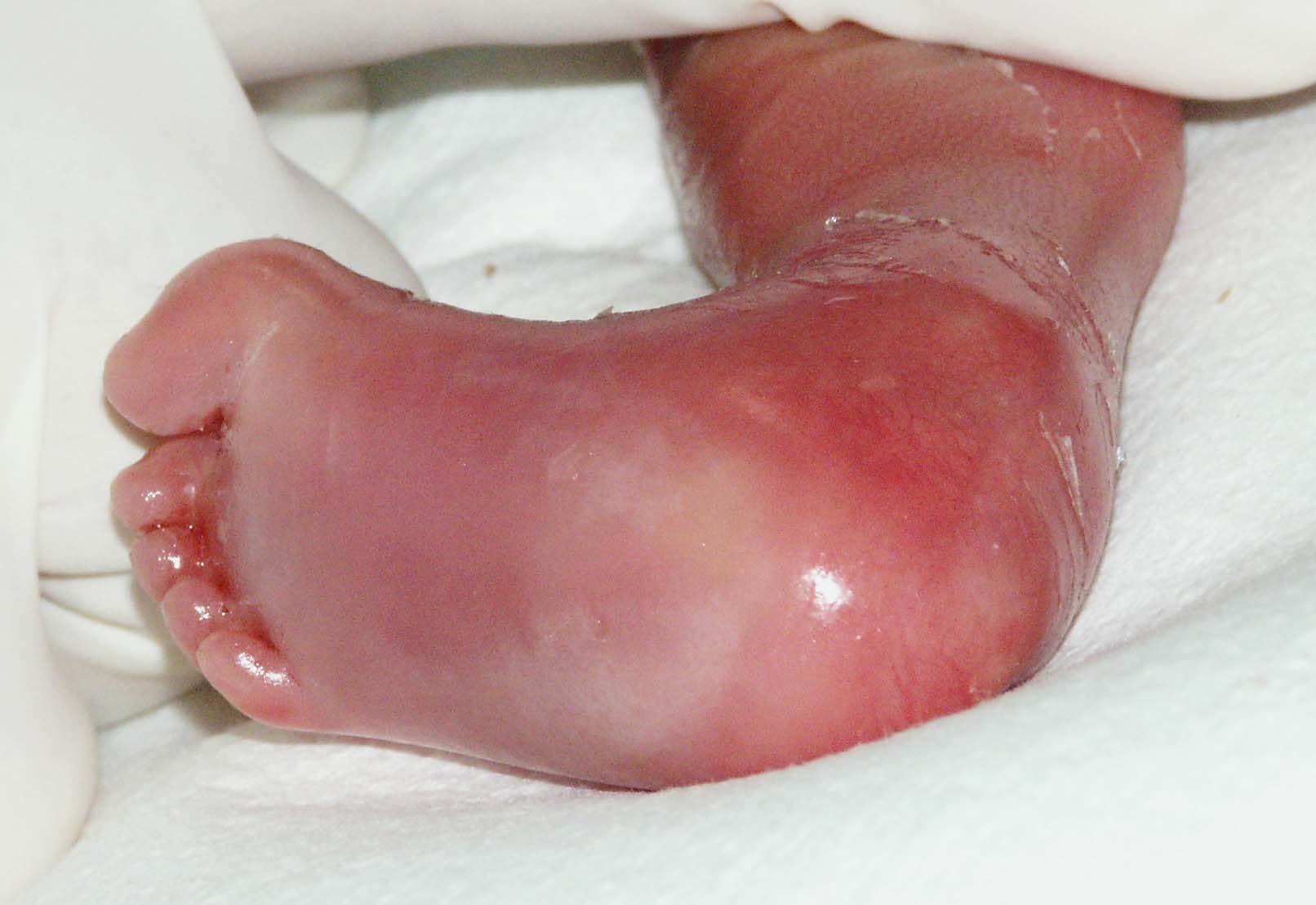 Ichthyosis is a family of genetic skin disorders characterized by dry, scaling skin that may be thickened or very thin. Harlequin ichthyosis is the most severe form of congenital ichthyosis. It is also known as "Harlequin baby," Harlequin ichthyosis, ichthyosis congenita, Ichthyosis fetalis, keratosis diffusa fetalis, "Harlequin fetus," and "Ichthyosis congenita gravior". Harlequin ichthyosis is a recessively inherited genetic disorder.
Ichthyosis is a family of genetic skin disorders characterized by dry, scaling skin that may be thickened or very thin. Harlequin ichthyosis is the most severe form of congenital ichthyosis. It is also known as "Harlequin baby," Harlequin ichthyosis, ichthyosis congenita, Ichthyosis fetalis, keratosis diffusa fetalis, "Harlequin fetus," and "Ichthyosis congenita gravior". Harlequin ichthyosis is a recessively inherited genetic disorder.
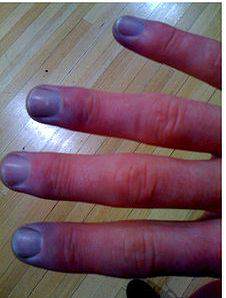 Named after a French physician Maurice Raynaud (1834–1881), the phenomenon is believed to be the result of vasospasms that decrease blood supply to the fingers, toes, and occasionally other areas/regions. The process is localized mainly in the upper limbs; lesion is usually bilateral and symmetrical.
Named after a French physician Maurice Raynaud (1834–1881), the phenomenon is believed to be the result of vasospasms that decrease blood supply to the fingers, toes, and occasionally other areas/regions. The process is localized mainly in the upper limbs; lesion is usually bilateral and symmetrical.
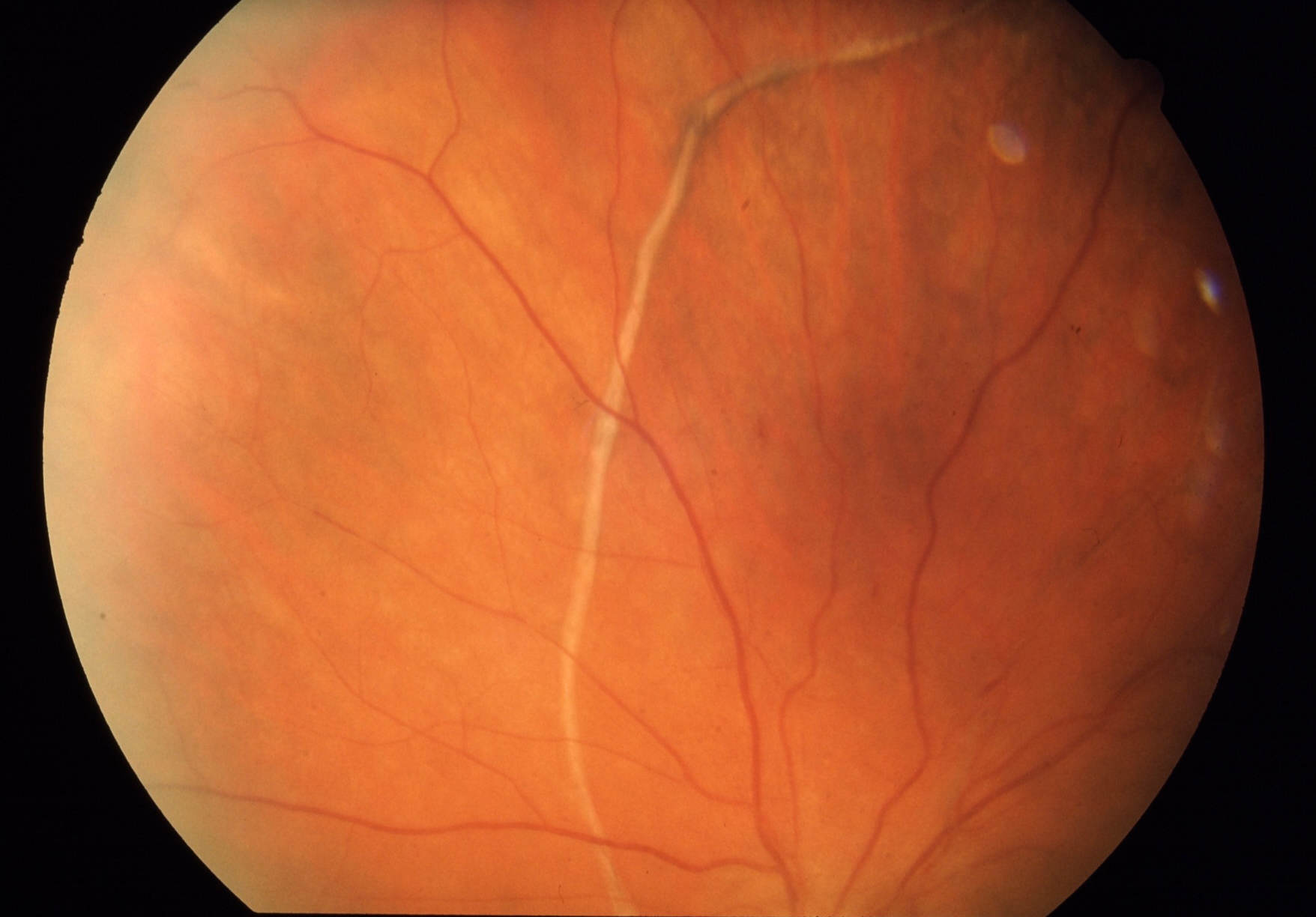 The retina is a thin, transparent tissue of light-sensitive nerve fibers and cells. It covers the inside wall of the eye the same as wallpaper covers the walls of a room.
The retina is a thin, transparent tissue of light-sensitive nerve fibers and cells. It covers the inside wall of the eye the same as wallpaper covers the walls of a room.
Retinal detachment (RD) was first recognized in the early 1700s by de Saint-Yves. Retinal detachment refers to separation of the inner layers of the retina from the underlying retinal pigment epithelium.
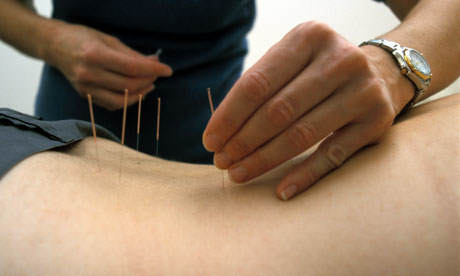 Acute pain such as labor pain hastwo dimensions: a sensory or physical dimension, with the transmissionof information, the pain stimuli, to the brain, and an affectivedimension due to interpretation of these stimuli through theinteraction of a wide variety of emotional, social, culturaland cognitive variables unique to the individual.
Acute pain such as labor pain hastwo dimensions: a sensory or physical dimension, with the transmissionof information, the pain stimuli, to the brain, and an affectivedimension due to interpretation of these stimuli through theinteraction of a wide variety of emotional, social, culturaland cognitive variables unique to the individual.
 Polycystic Ovary Syndrome affects an estimated 5-10 percent of women of childbearing age and it is a leading cause of infertility(due to infrequent or lack of ovulation). It is the most common hormonal disorder among women of reproductive age.
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome affects an estimated 5-10 percent of women of childbearing age and it is a leading cause of infertility(due to infrequent or lack of ovulation). It is the most common hormonal disorder among women of reproductive age.
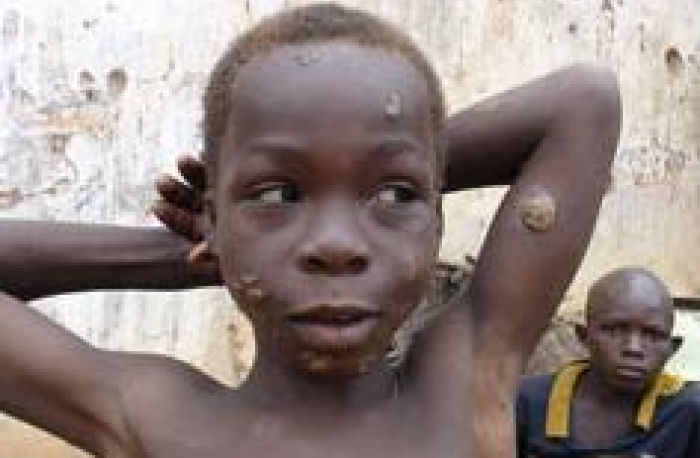 Like endemic syphilis and pinta, yaws (also known as framboesia tropica and pian) is a form of non-venereal treponematoses. The causative organism Treponema pallidum subsp pertenue is morphologically and serologically identical to T pallidum ssp pallidum (syphilis). Like syphilis, yaws has different s tages of disfig urement. However, unfortunately for the kids, yaws is not spread by sexual contact. The major route of infection is through direct person-to-person contact.
Like endemic syphilis and pinta, yaws (also known as framboesia tropica and pian) is a form of non-venereal treponematoses. The causative organism Treponema pallidum subsp pertenue is morphologically and serologically identical to T pallidum ssp pallidum (syphilis). Like syphilis, yaws has different s tages of disfig urement. However, unfortunately for the kids, yaws is not spread by sexual contact. The major route of infection is through direct person-to-person contact.