Raynaud's Disease
- font size decrease font size increase font size
 Named after a French physician Maurice Raynaud (1834–1881), the phenomenon is believed to be the result of vasospasms that decrease blood supply to the fingers, toes, and occasionally other areas/regions. The process is localized mainly in the upper limbs; lesion is usually bilateral and symmetrical.
Named after a French physician Maurice Raynaud (1834–1881), the phenomenon is believed to be the result of vasospasms that decrease blood supply to the fingers, toes, and occasionally other areas/regions. The process is localized mainly in the upper limbs; lesion is usually bilateral and symmetrical.
The disease occurs usually in young women, accompanied by a pronounced microcirculatory disorders. The main manifestation of the disease is intermittent generalized spasm -above arteries with subsequent degenerative changes in the walls of arteries and capillaries, thrombosis of terminal arteries.
The main causes of Raynaud's disease is the long perfrigeration, chronic trauma of fingers, impairment of the function of some endocrine organs (thyroid, gonads), heavy mental disorders. "Starter" Mechanisms in disease development are violations of the vascular innervation.
There are three stages of the disease.
Stage 1 - angiospastic. Characterized by a pronounced increase vascular tone. There are intermittent spasms of vessels terminal phalanges. Fingers (usually II and III) hands are deadly pale, cold to the touch and insensitive. A few minute changes to the expansion of vascular spasm. Due to the active hyperemia
comes redness and fingers are warm. The sick note a strong burning sensation and sharp pain, swelling appears in mezaphalanges joints. When vascular tone is normalized, finger colouration becomes normal, the pain disappears.
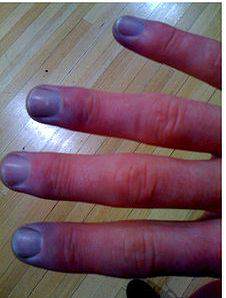
Stage II - angioparalytic. Attacks of blanching ("dead thumb ") at this stage is rarely repeated, hands and fingers become bluish coloration, and by lowering hands down, this colouration is enhanced and take purple hue. Swelling and cyanosed fingers become constant. Duration of stages I-II, on Average 3-5 years.
Stage III - trophoparalytic. On the fingers appear panaritiums and ulcers. Formation of necrotic foci, soft tissue exciting one-two terminal phalanges of the finger less. With the development of emarcation begins rejection of necrotic areas, and then remain slow healing ulcers, scars of which have a pale color, painful, fused with the bone.
Treatment. Demonstrates the use of angiotrophic drugs and antispasmodics, physiotherapy, hyperbaric oxygenation. In the event of conservative treatment ineffectiveness, thoracic or lumbar sympathectomy or stellectomy is performed (depending on the location of the lesion).
