Williams syndrome
- font size decrease font size increase font size
Is William’s syndrome a blessing in disguise? People with Williams are considered a ‘Highly musical species’.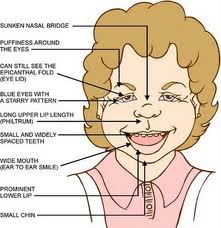
Williams disease affects approximately 1 in 10,000 people worldwide. It is a rare genetic disorder that affects a child's growth, physical appearance, and cognitive development. The syndrome was originally described independently by Williams and Beuren in 1961, hence the name.
PATHOPHYSIOLOGY
Like Down's syndrome it is caused by an abnormality in chromosomes (specifically deletion of chromosome 7 leading to lack of elastin gene) and shows a wide variation in ability from person to person.
The elastin gene's protein product gives blood vessels the stretchiness and strength. It’s absence leads to abnormalities that involve local or diffuse stenosis of the medium-sized or large-sized arteries, most commonly in the ascending aorta above the aortic valves or in the pulmonary arteries. Though rare, stenosis of the descending aorta, intracranial arteries, and renal arteries do occur.
It is a non-hereditary syndrome which occurs at random although it is possible for a child to inherit a broken chromosome from a parent who also had the disorder.
CLINICAL FEATURES
Unlike disorders that can make connecting with your child difficult, children with Williams syndrome tend to be social, friendly and endearing. The major huddle faced by people with Williams is cardiovascular diseases, a part of connective tissue pathology, which accounts for most cases of early mortality. A wide phenotypic spectrum is observed in the syndrome.
Most children and adults with Williams syndrome have some combination of the following "Elfin facies" facial dysmorphology, attributed to the elastin gene haploinsufficiency: short upturned nose, flat nasal bridge, long philtrum, flat malar area, wide mouth, full lips, dental malocclusion and widely spaced teeth, micrognathia, and periorbital fullness. A stellate, lacy pattern of the irises can be observed in children with blue eyes. Facial features become more apparent with age.{youtube}xC2j4HoWimE{/youtube}
Nails tend to be hypoplastic and the skin soft and lax, and the halluces have a valgus deviation.
Other symptoms include: low birth weight, often after being "late for dates", slow weight gain. Sometimes weight loss; below average growth; very slow feeding, restless sleeping, and irritability; sometimes a hernia, a squint and excessive vomiting leading to dehydration and constipation, mild-to-moderate mental retardation. A raised calcium level is found in some babies (hypercalcemia). They also tend to exhibit, hypersensitivity to noise, Hyperactivity in early years, phobias, panic attacks, and depression, interest and enthusiasm for music, connective tissue disorders.
DIAGNOSIS
The syndrome can be identified by its distinctive physical characteristics. To confirm the diagnosis, fluorescent in situ hybridization (FISH) is performed, since the deletion is too small therefore can’t be seen in a karyotype.
TREATMENT
There is no cure for Williams syndrome. Management of Williams syndrome is tailored specifically to the presenting clinical spectrum. Therefore cardiovascular diseases, hypercalcemia, systemic hypertension are monitored and treated accordingly.

